In brief
- Multiverse’s CompactifAI tech reportedly slashed parameter count by 70% and model memory by 93%, while preserving 97–98% accuracy.
- The company just closed a $215M Series B round backed by Bullhound Capital, HP Tech Ventures, and Toshiba.
- The method uses tensor networks from quantum physics to compress models and “heals” them with fast retraining, claiming 50% faster performance at inference.
A Spanish AI startup has just convinced investors to hand over $215 million based on a bold claim: they can shrink large language models by 95% without compromising their performance.
Multiverse Computing’s innovation hinges on its CompactifAI technology, a compression method that borrows mathematical concepts from quantum physics to shrink AI models down to smartphone size.
The San Sebastian company says that their compressed Llama-2 7B model runs 25% faster at inference while using 70% fewer parameters, with accuracy dropping just 2-3%.
If validated at scale, this could address AI’s elephant-sized problem: models so massive they require specialized data centers just to operate.
“For the first time in history, we are able to profile the inner workings of a neural network to eliminate billions of spurious correlations to truly optimize all sorts of AI models,” Román Orús, Multiverse’s chief scientific officer, said in a blog post on Thursday.
Bullhound Capital led the $215 million Series B round with backing from HP Tech Ventures and Toshiba.
The Physics Behind the Compression
Applying quantum-inspired concepts to tackle one of AI’s most pressing issues sounds improbable—but if the research holds up, it’s real.
Unlike traditional compression that simply cuts neurons or reduces numerical precision, CompactifAI uses tensor networks—mathematical structures that physicists developed to track particle interactions without drowning in data.
The process works like an origami for AI models: weight matrices get folded into smaller, interconnected structures called Matrix Product Operators.
Instead of storing every connection between neurons, the system preserves only meaningful correlations while discarding redundant patterns, like information or relationships that are repeated over and over again.
Multiverse discovered that AI models aren’t uniformly compressible. Early layers prove fragile, while deeper layers—recently shown to be less critical for performance—can withstand aggressive compression.
This selective approach lets them achieve dramatic size reductions where other methods fail.
After compression, models undergo brief “healing”—retraining that takes less than one epoch thanks to the reduced parameter count. The company claims this restoration process runs 50% faster than training original models due to decreased GPU-CPU transfer loads.
Long story short—per the company’s own offers—you start with a model, run the Compactify magic, and end up with a compressed version that has less than 50% of its parameters, can run at twice the inference speed, costs a lot less, and is just as capable as the original.
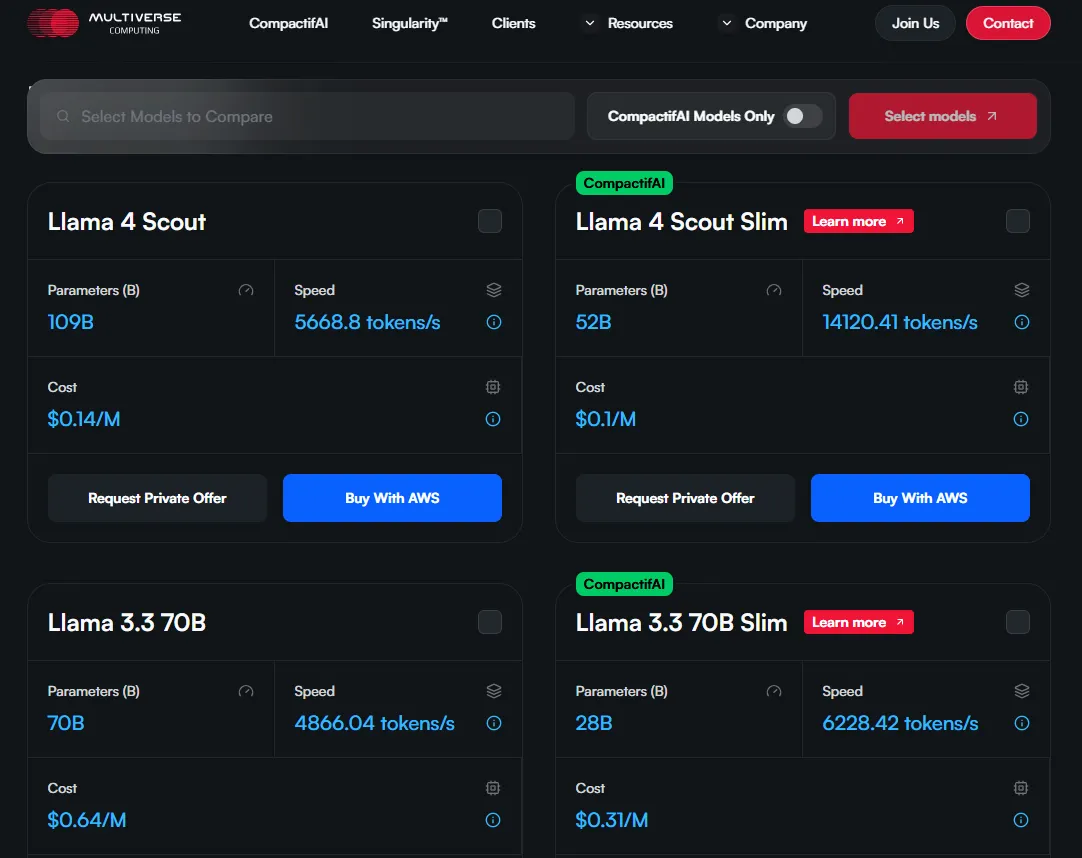
In its research, the team shows you can reduce the Llama-2 7B model’s memory needs by 93%, cut the number of parameters by 70%, speed up training by 50%, and speed up answering (inference) by 25%—while only losing 2–3% accuracy.
Traditional shrinking methods like quantization (reducing the precision like using fewer decimal places), pruning (cutting out less important neurons entirely, like trimming dead branches from a tree), or distillation techniques (training a smaller model to mimic a larger one’s behavior) are not even close to achieving these numbers.
Multiverse already serves over 100 clients including Bosch and Bank of Canada, applying their quantum-inspired algorithms beyond AI to energy optimization and financial modeling.
The Spanish government co-invested €67 million in March, pushing total funding above $250 million.
Currently offering compressed versions of open-source models like Llama and Mistral through AWS, the company plans to expand to DeepSeek R1 and other reasoning models.
Proprietary systems from OpenAI or Claude remain obviously off-limits since they are not available for tinkering or study.
The technology’s promise extends beyond cost savings measures. HP Tech Ventures’ involvement signals interest in edge AI deployment—running sophisticated models locally rather than cloud servers.
“Multiverse’s innovative approach has the potential to bring AI benefits of enhanced performance, personalization, privacy and cost efficiency to life for companies of any size,” Tuan Tran, HP’s President of Technology and Innovation, said.
So, if you find yourself running DeepSeek R1 on your smartphone someday, these dudes may be the ones to thank.
Edited by Josh Quittner and Sebastian Sinclair
Generally Intelligent Newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI model.
News source: Big Brains, Tiny Models: Spain’s Multiverse Computing Bags $215M to Shrink AI for Smartphones
Read the full article and more directly from the source!
Enjoying our initiative? Support us with a BTC donation:
BTC Wallet: bc1q0faa2d4j9ezn29uuf7c57znsm5ueqwwfqw9gde


